What You Will Do:

- Watch the Khan Academy video: "Boyle's Law" and review related concepts.
- Explore how the microscopic impacts of gas particles account for the pressure of a gas.
- Collect pressure data in the Desmos Graphing Calculator for decreasing volume of a hand syringe.
- Build a mathematical model of the relationship between volume and pressure.
- Complete the Google Docs worksheet: "Boyle's Law" and turn it in according to your teacher's directions.
- Gas particles: tiny molecules that move in constant, random motion.
- Pressure: the total force from countless microscopic impacts of gas particles hitting the walls of a container.
- Volume: the amount of space available for gas particles to move around in.
- Collision rate: how often gas particles strike the container walls; higher collision rates mean higher pressure.
- Click to watch this Khan Academy video to learn more about these concepts.

- Click this link Boyle’s Law Worksheet to open the worksheet. If your class uses Google Classroom, open the worksheet from your assignment. If not, click the link above, choose Make a copy, complete your work, and turn it in the usual way.
- Click the Show Directions button in the upper-right corner to learn how to collect data for this activity.
- Observe the motion of the particles in the simulation below and how they impact the inside of the syringe. Imagine a handful of tiny pebbles hitting your hand in a similar way. What would you feel from all of those impacts?
- Click the syringe's minus (-) button to reduce the volume the particles move within and observe the effect on the impact rate of the particles.
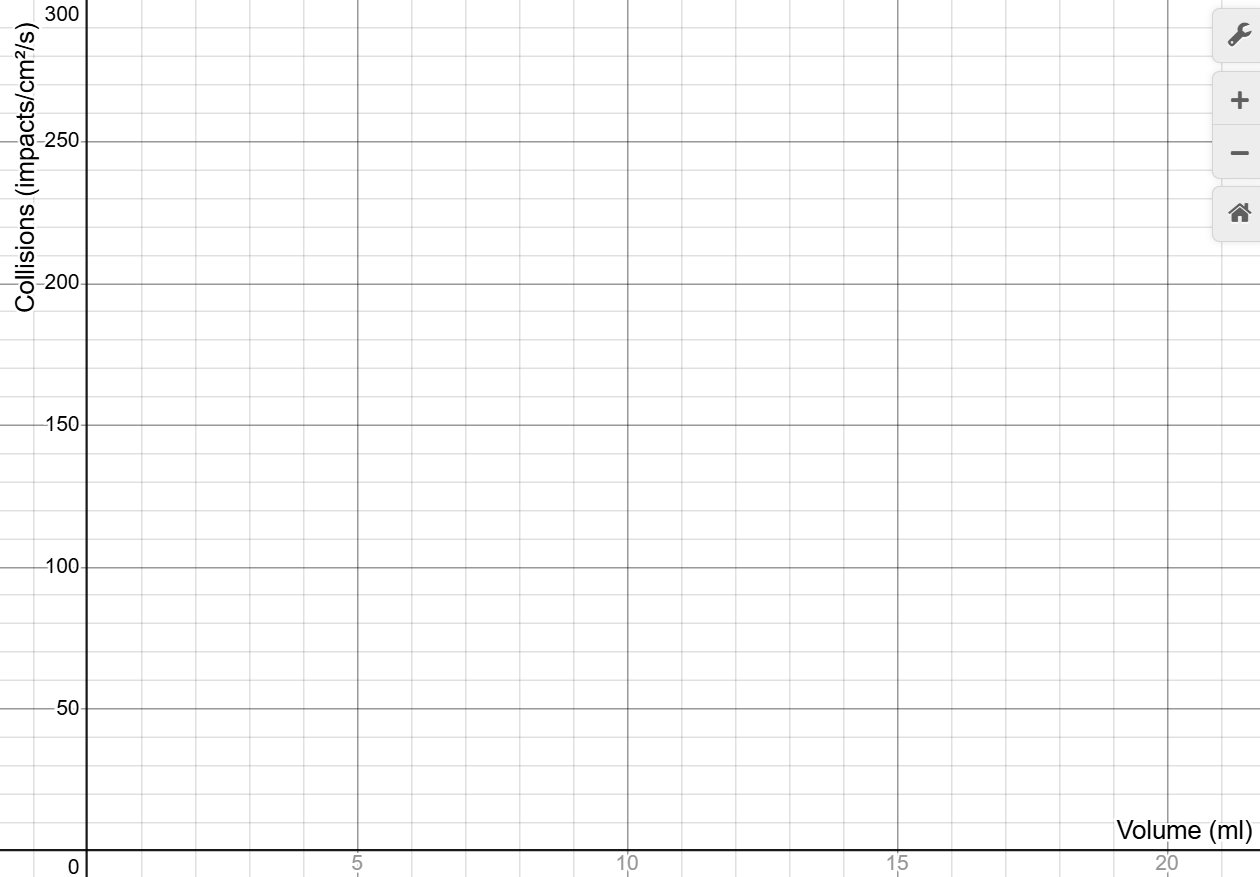
- Repeat reducing the volume by 2 mL and allowing the impact rate to settle. Imagine what a graph with volume on the horizontal axis and impact rate on the vertical axis would look like.
- Use your mouse to click and drag on the graph to draw your prediction. If you need to start over, click Erase Drawing. When you are satisfied, click Capture Drawing to copy the image to the clipboard and paste it into the Boyle's Law worksheet and answer the related questions.
20 mL
Collisions = 0.00 Impacts/cm²/s